Genome Instability & Disease Volume 5. Issue 6 & Volume 6. Issue 1 简介
1. DNA damage and chromatin rearrangement in promoting neurodegeneration: role of hallmark proteins| Angeline Julius, Suresh Malakondaiah & Raghu Babu Pothireddy
Studies have shown that neurodegenerative diseases are closely related to DNA damage and chromatin reorganization caused by genetic and environmental factors. In this review, Dr. Angeline Julius and her colleagues from the Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research in India introduce hallmark proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases and examine their regulatory roles in maintaining chromatin structure stability and DNA damage repair. They also highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting epigenetic mechanisms—such as using HDAC inhibitors or modulating microRNAs—to restore genomic stability and improve disease outcomes.
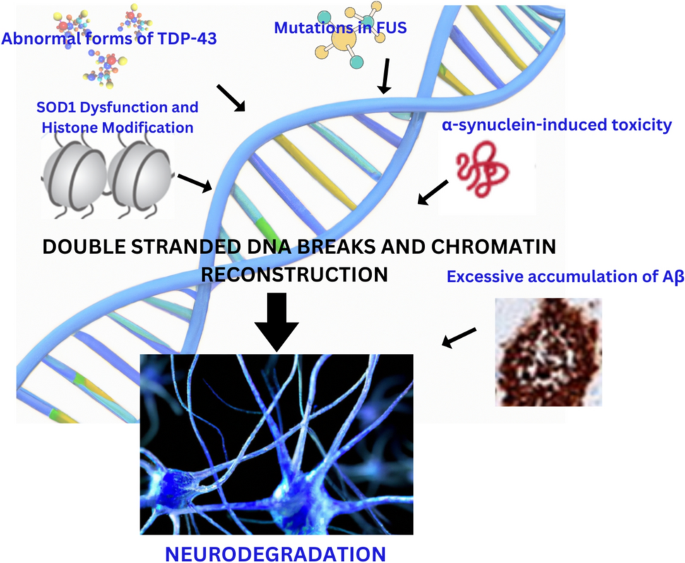
Hallmark proteins involved in neurodegeneration
研究表明,神经退行性疾病与遗传和环境等因素导致的DNA损伤和染色质结构改变密切相关。来自印度巴拉斯高等教育研究学院的Angeline Julius博士等人向我们介绍了神经退行性疾病的一些标志蛋白,以及这些蛋白在维持染色质结构稳定和DNA损伤修复中的调节作用,为此类疾病的治疗提供参考。
 Dr. Angeline Julius
Dr. Angeline Julius
全文链接://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-024-00142-8
2. Identification of novel phytotherapeutic agents for understanding hypertrophic cardiomyopathy via genetic mapping and advanced computational analysis | Abdullahi Tunde Aborode, Onifade Isreal Ayobami, Ammar Usman Danazumi, Christopher Busayo Olowosoke, Haruna Isiyaku Umar, Abraham Osinuga, Aeshah A. Awaji, Fatmah Ali Awaji, Ebenezer Ayomide Omojowolo, Najwa Ahmad Kuthi, Tanveer Shaikh, Babatunde Shuaib Anidu, Athanasios Alexiou, Ridwan Olamilekan Adesola, Zainab Olapade, Awah Favour Matthew, Blessing Ameh, Toluwalope Yinka Oni, Adetolase Azizat Bakre & Godfred Yawson Scott
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a monogenic cardiovascular disease. Here, Dr. Godfred Yawson Scott from Kwame Nkrumah University of Technology in Ghana and his colleagues studied the genetic landscape of HCM using computational algorithms and identified several bioactive compounds with therapeutic potential. The interaction between these phytochemicals and the MYH7 missense mutation showed that they inhibited MYH7 overactivity by blocking specific active site residues, thereby reducing the risk of end-stage heart failure and premature death, thus offering new insights into HCM treatment. The study also revealed novel gene–phenotype associations and suggested that genes linked to channelopathies may act as genetic modifiers influencing the severity and clinical presentation of HCM.
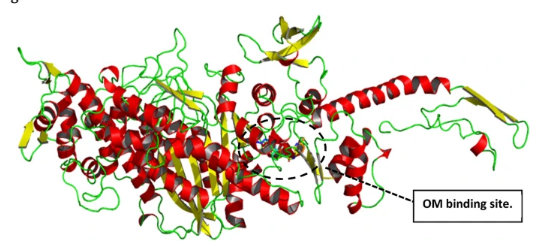 The 3D structure of the mutated human-cardiac myosin motor domain in the presence of a known activator, Omecamtiv mecarbil (OM).
The 3D structure of the mutated human-cardiac myosin motor domain in the presence of a known activator, Omecamtiv mecarbil (OM).
肥厚型心肌病(HCM)是一种单基因心血管疾病,来自加纳Kwame Nkrumah 理工大学的Godfred Yawson Scott博士和他的同事通过计算机算法研究HCM的遗传图谱,鉴定了一些具有治疗HCM潜力的生物活性化合物,这些植物化学物质与MYH7错义突变之间的相互作用表明它们通过阻断特定的活性位点残基来抑制MYH7的过度活性,进而降低终末期心力衰竭和过早死亡的发生率,为HCM治疗提供参考。

Dr. Godfred Yawson Scott
全文链接://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-024-00141-9
3. Identification of potential targets of chrysin in treating HSV-1 infection: a network pharmacology study | Junxian Liu, Housheng Zheng, Jian Zhou, Liang Ye & Lu Wang
Chrysin has anti-HSV-1 (herpes simplex virus type 1) activity, but the underlying mechanism is unclear. Now, Professor Liang Ye and colleagues at Shenzhen University have used the SEA, Swiss, and PharmMapper databases to predict and verify the therapeutic effects of chrysin against HSV-1 and identified potential molecular targets involved in its antiviral action. Through a combination of network pharmacology and molecular docking, they revealed that chrysin may exert its effects by binding to key hub genes such as SRC, VEGFA, EGFR, and PARP1, offering a new reference point for improving antiviral efficacy in patients with HSV-1 infection.
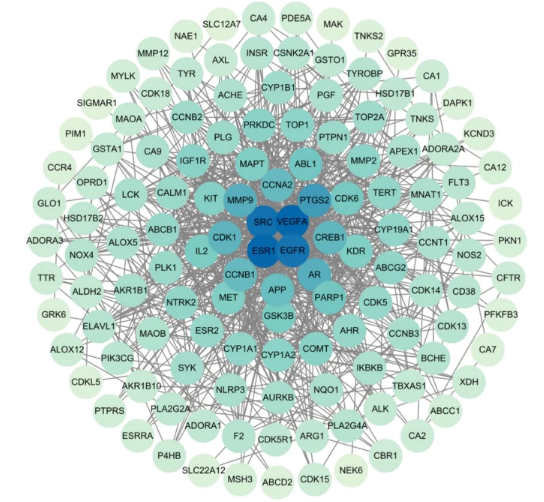 The potential targets of chrysin (circles); dark circles close to the center have the highest level of relevance.
The potential targets of chrysin (circles); dark circles close to the center have the highest level of relevance.
白杨素在既有的研究中具有抗HSV-1疱疹病毒活性,但其作用机制尚不清楚。草莓视频 的叶亮教授通过利用SEA、Swiss和Pharmapper等数据库预测和验证了白杨素对HSV-1的治疗作用,确定了白杨素在抗HSV-1感染中的潜在分子靶点,为提高HSV-1感染患者的抗病毒疗效提供了新思路。

Pro. liang Ye
全文链接://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-024-00140-w
4. Photodynamic therapy-triggered nuclear translocation of berberine from mitochondria leads to liver cancer cell death| Wencheng Wei, Hao Wang, Lisha Ai & Hui Liu
Berberine is a traditional Chinese herbal compound known for its anticancer and phototoxic properties. Here, Dr. Hui Liu and colleagues from Shenzhen University General Hospital investigated the phototoxic effects of berberine under blue light (488 nm) and found that berberine rapidly translocates from the mitochondria to the nucleus upon light exposure, ultimately inducing cell death in SNU449 and Huh7 liver cancer cells. Their findings suggest that berberine could serve as a photosensitizer to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT) for liver cancer. The study also revealed that berberine-PDT treatment leads to increased oxidative stress, cell cycle arrest, and activation of pro-apoptotic pathways, highlighting its potential as a novel strategy for liver cancer treatment.
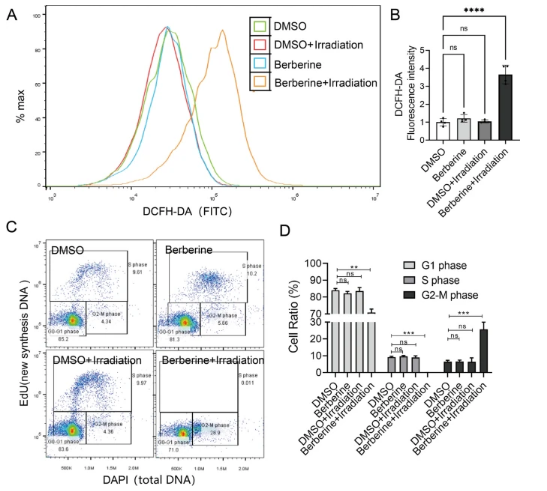
Effects of berberine combined with PDT on cellular ROS and cell cycle arrest in SNU449 cells.
小檗碱是一种具有抗癌和光毒性作用的中草药,草莓视频 总医院的刘辉医生和同事,通过检测小檗碱在蓝光(488 nm)照射下的光毒性效应,发现小檗碱在光照下可迅速从线粒体转运至细胞核,最终导致SNU449和Huh7细胞死亡,提示小檗碱可作为光敏剂,增强PDT对肝癌的治疗效果。
 Hui Liu
Hui Liu
全文链接: //link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-024-00145-5
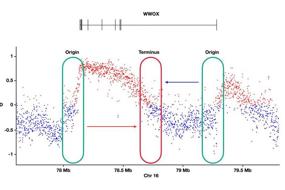
5. Quantitative crotonylome analysis reveals that crotonylation of splicing factors is involved in DNA damage response| Zhiling Chen, Kaiping Hou, Hongyin Zhang, Yunkun Zhang, Yinan Na & Hailong Wang
Lysine crotonylation (Kcr) is a newly identified post-translational modification, but its role in regulating the DNA damage response (DDR) is unclear. In this latest study, Professor Hailong Wang and colleagues from Beijing Normal University used quantitative proteomics to identify numerous Kcr-modified proteins regulated during the DDR process and highlighted the key involvement of RNA splicing factors. They identified >590 Kcr sites with increased levels and >330 sites with decreased levels following etoposide-induced DNA damage. This work constitutes the first comprehensive map of Kcr dynamics in the DDR and underscoring the potential regulatory role of RNA-related proteins in genome stability.
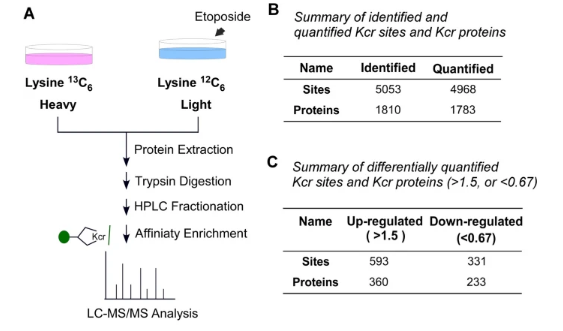
Systematic profiling of DNA damage-induced lysine crotonylation (Kcr).
赖氨酸巴豆酰化(Kcr)是一种新兴的翻译后修饰,在DNA损伤反应(DDR)调控的作用尚未完全阐明,来自北京师范大学的王海龙教授和同事通过定量蛋白质组学鉴定了一批在DDR过程中调控的Kcr蛋白,并指出RNA剪接因子在这一过程中的关键作用。
 Prof. Hailong Wang
Prof. Hailong Wang
全文链接: //link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-024-00143-7
6. The transcriptional dysregulation of choline catabolism genes was implicated in HCC stage-specific carcinogenesis| Karthik Balakrishnan
Choline catabolism is closely associated with cancer progression. Here, Dr. Karthik Balakrishnan from the Saroj Institute of Technology and Management (SITM) in India analyzed mRNA expression profiles from TCGA and liver cancer tissues to investigate the transcriptional activity of choline catabolism genes in pan-cancer datasets. The study found that these genes were significantly activated in stage -specific hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). ROC curve analysis demonstrated high specificity and sensitivity for these genes in HCC tumors, while overall survival analysis confirmed their association with poor prognosis in HCC patients. Further analysis identified these genes as essential for phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis, a process critical for membrane formation during cell proliferation. These findings suggest that genes involved in choline catabolism may serve as potential therapeutic targets for liver cancer.
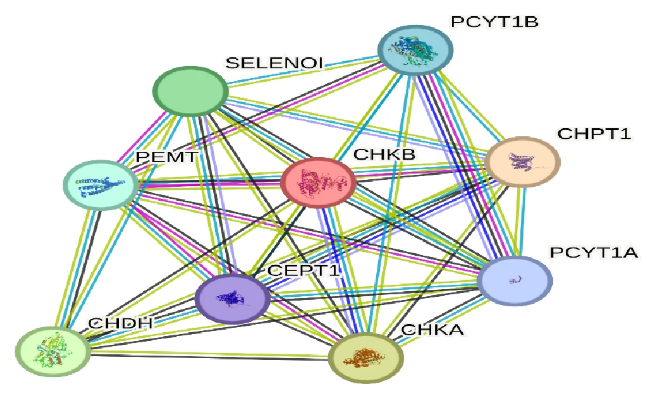 Protein–protein interaction network using STRING reveals functional coordination of choline catabolic pathway proteins in HCC.
Protein–protein interaction network using STRING reveals functional coordination of choline catabolic pathway proteins in HCC.
胆碱分解代谢与癌症发展密切相关,来自印度Saroj技术与管理学院(SITM)的 Karthik Balakrishnan博士利用TCGA和肝癌组织中的mRNA表达谱,研究了泛癌组织中胆碱分解代谢基因的转录情况,发现胆碱分解代谢基因在阶段特异性肝细胞癌(HCC)中显著激活,ROC曲线分析显示这些基因在分期特异性HCC肿瘤中具有更高的特异性和敏感性。总体生存研究也证实这些基因和HCC患者的不良预后相关。这些发现提示胆碱分解代谢的相关基因可以作为肝癌治疗重点关注的靶标。
全文链接: //link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00146-y
7. Increased NINJ1 expression in hormone receptor-positive breast tumors: implications for prognosis| Caglar Berkel
NINJ1 (ninjurin 1) has primarily been associated with mediating plasma membrane rupture (PMR) during the lytic phase of various programmed cell death pathways, but its role in breast cancer has not been explored. Now, Dr. Caglar Berkel from Tokat Gaziosmanpasa University in Turkey has analyzed data from the TCGA-BRCA dataset and used the Kaplan–Meier Plotter tool to assess cancer genome expression and patient survival. He found that higher NINJ1 expression in estrogen receptor-positive and progesterone receptor-positive breast cancer patients was associated with improved survival outcomes, suggesting NINJ1 may serve as a potential immunotherapy target. Notably, triple-negative breast cancer—a more aggressive subtype—showed the lowest NINJ1 expression, further supporting its potential relevance in subtype-specific treatment strategies.
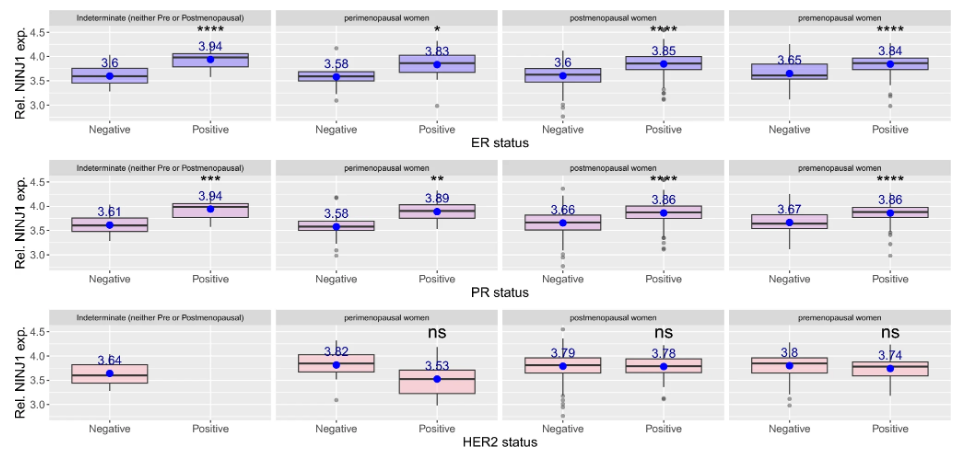
Higher NINJ1 expression observed in ER-positive or PR-positive breast cancer cells does not depend on menopausal status.
NINJ1(Ninjurin 1)在已知的研究中主要介导裂解期的质膜破裂(PMR),以响应各种程序性细胞死亡机制的诱导物,未见有和乳腺癌相关的报道。来自土耳其托卡特Gaziosmanpasa大学的Caglar Berkel博士利用TCGA-BRCA数据库和Kaplan–Meier Plotter 工具分别研究了癌症基因组图谱和患者生存率,发现ER阳性和PR阳性的乳腺癌患者中,较高的NINJ1水平有助于提高患者的生存率,提示NINJ1可能可以作为乳腺癌免疫治疗的靶标。

Dr. Caglar Berkel
全文链接: //link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00150-2
8. Screening and function analysis of key genes and signaling pathways in Alzheimer’s disease via next generation sequencing data analysis and bioinformatics approaches| Basavaraj Vastrad & Chanabasayya Vastrad
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder marked by the accumulation of extracellular senile plaques. Using an integrated bioinformatics approach—including next-generation sequencing, the limma-R Bioconductor package, HIPPIE protein interaction database, Cytoscape network analysis, and ROC curve evaluation—Basavaraj Vastrad and Chanabasayya Vastrad from Chanabasava Nilaya, India, identified Hsa-mir-4517, Hsa-mir-3652, EGR1, and ZNF354C as potential key microRNAs and transcription factors involved in AD progression. Their analysis also revealed 956 differentially expressed genes enriched in neuronal signaling pathways and membrane-associated functions. These findings offer valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms of AD and propose reliable genetic markers and regulatory pathways for diagnosis, prognosis, and the development of targeted therapies.
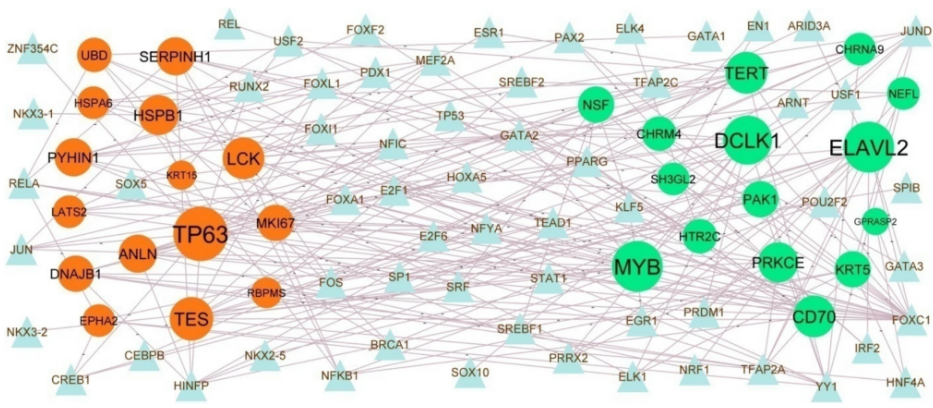
TF-hub gene regulatory network. The blue color triangle nodes represent the key TFs; up regulated genes are marked in green; down regulated genes are marked in red.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种以细胞外老年斑为特征的神经退行性疾病。来自印度Chanabasava Nilaya的Basavaraj Vastrad 和 Chanabasayya Vastrad通过对下一代测序(NGS)数据集, limma-R生物导体包,HIPPIE,Cytoscape,受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价等多种生物信息学手段进行综合分析,发现Hsa-mir-4517、Hsa-mir-3652、EGR1和ZNF354C可能是AD进展的关键miRNAs和TFs,为AD的分子机制、诊断、预后和候选靶向治疗提供了可靠的关键基因和信号通路。
全文链接://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00147-x
9. A groundbreaking achievement in genomics: the complete telomere-to-telomere sequence of a mouse genome | Wei-Guo Zhu
As one of the most widely used model organisms, mice offer valuable genetic resources for biomedical research. In a groundbreaking study, Professor Xiaochun Yu and his colleagues at West Lake University sequenced and assembled the first complete telomere-to-telomere map of the mouse genome by integrating multiple advanced genome sequencing technologies. Their work, recently published in Science, resolves long-standing limitations of the previous GRCm39 reference genome, which left about 8% of the genome—particularly repetitive and functionally important regions such as ribosomal DNA arrays, pericentromeric, and subtelomeric regions—unsequenced. In this commentary, Professor Wei-guo Zhu of Shenzhen University provides his thoughts on this work, emphasizing how the results that deliver a more complete and accurate reference genome for Mus musculus, will accelerate progress in both basic and applied genetic research.
作为广泛使用的模式动物,小鼠具有重要的遗传资源。西湖大学的俞晓春教授团队通过整合多项先进的基因组测序技术,对小鼠基因组进行了测序和组装,获得了迄今为止最完整的从端粒到端粒的基因组图谱,相关成果近期发表于Science期刊。草莓视频 的朱卫国教授对此进行点评,指出该研究克服以前装配的局限性,为小家鼠提供了更完整和准确的参考,不仅提高了小鼠基因组的保真度,而且为今后对其他复杂基因组进行全序列测定开创了先例,为深入了解遗传学和疾病铺平了道路。

Prof. Wei-Guo Zhu
全文链接: //link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-024-00144-6

用户登录
还没有账号?
立即注册