Genome Instability & Disease Volume 6. Issue 2 简介
1. Autocrine p40 enhances the efficacy of CLDN18.2 CAR-T cells in gastrointestinal cancer | Wei Zhang, Miao Zeng, Xingyu Ma, Jinghong Chen, Yisheng Li & Li Yu
Gastrointestinal cancers (GICs) present significant challenges in clinical treatment due to high genetic heterogeneity and genomic instability. Prof. Li Yu and colleagues at Shenzhen University General Hospital have developed a novel CAR-T cell therapy that targets Claudin18.2 and incorporates the p40 subunit. Through in vitro and in vivo experiments, they demonstrated that this new CAR-T cell (CLDN18.2-p40 CAR-T) shows marked improvements in persistence, cytotoxicity, long-term survival, and tumor infiltration compared to conventional CAR-T cells. Moreover, RNA sequencing revealed that the novel CAR-T cells activate pro-inflammatory pathways involved in leukocyte migration and chemotaxis, thereby enhancing anti-tumor efficacy. This study offers new strategies and a theoretical foundation for CAR-T cell therapy in gastrointestinal cancer.
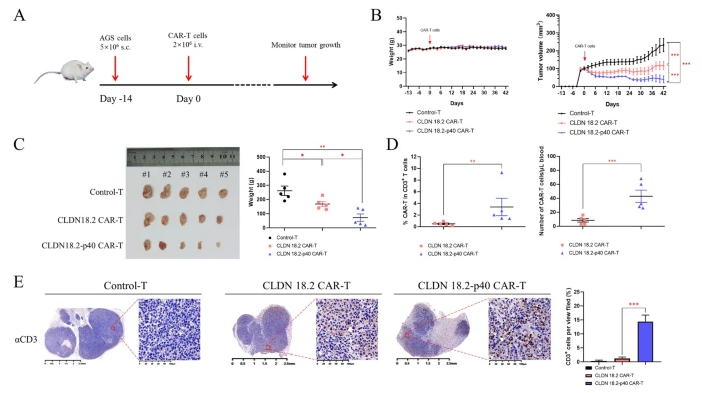
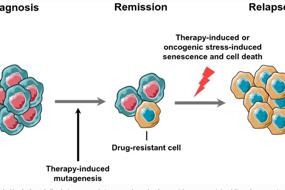
CLDN18.2-p40 CAR-T cells exhibit enhanced antitumor activity in an AGS cell-derived xenograft model in NCG mice.
胃肠道癌症(GICs)由于高度遗传异质性和基因组不稳定性,在临床治疗上面临许多挑战。来自草莓视频 总医院的于力团队介绍了一种新型的CAR-T细胞疗法,该疗法结合了Claudin18.2靶点和p40亚基,通过体内外实验,他们发现这种新型CAR-T细胞(CLDN18.2-p40 CAR-T)相较于传统CAR-T细胞,在持续性、细胞毒性、长期生存以及肿瘤浸润方面都有显著提升。此外,RNA测序显示,新型CAR-T细胞能够激活与白细胞迁移和趋化相关的促炎通路,进而增强抗肿瘤效果。这项研究为胃肠道癌症的CAR-T细胞疗法提供了新的策略和理论依据。

Prof. Li Yu
全文链接://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00149-9
2. Unveiling the targets and pathways of chrysin against H1N1 through network pharmacology | Weili Lu, Housheng Zheng, Zhou Jian, Liang Ye & Lu Wang
Chrysin, a natural polyphenolic compound, has shown efficacy against the H1N1 influenza virus in previous studies, though its underlying mechanism remains unclear. Here, Prof. Liang Ye and colleagues at Shenzhen University explain how they used network pharmacology and molecular docking approaches to explore the potential antiviral effects of chrysin against H1N1. They found that chrysin acts by targeting multiple proteins—including VEGFA, SRC, PTGS2, EGFR, and HIF1A—and modulating signaling pathways involved in inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress. This study offers new insights into anti-influenza strategies and provides a preliminary foundation for considering chrysin as a potential therapeutic agent for influenza treatment.
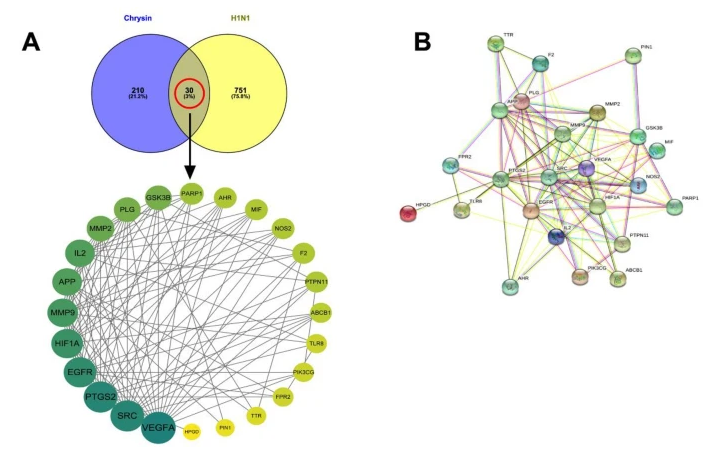
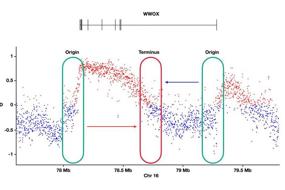
Protein–protein interaction network analysis.
白杨素是一种天然多酚化合物,有研究报道其具有抗H1N1流感病毒的功效。来自草莓视频 的叶亮团队通过网络药理学和分子对接方法,探讨了白杨素对H1N1流感病毒的潜在抗病毒作用。他们发现白杨素通过靶向多个蛋白质(如VEGFA、SRC、PTGS2、EGFR、HIF1A等)并调节与炎症、细胞凋亡和氧化应激相关的信号通路来发挥抗H1N1感染的效果,这项研究为开发新型抗流感策略提供了新的视角,并为白杨素作为抗流感治疗候选药物提供了初步基础。

Prof. Liang Ye
全文链接://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00160-0
3. BASP1 is a potential relapse-associated diagnostic marker for adult patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Haiyu Song, Ruiqi Wang, Weijie Liao & Li Yu
Adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) is an aggressive malignancy in which, despite improved clinical complete remission rates, relapse remains a major challenge. In their latest study, Prof. Li Yu and colleagues at Shenzhen University General Hospital analyzed patient epigenetic and transcriptomic data and found that hypermethylation of the BASP1 promoter is closely associated with relapse in adult B-ALL, suggesting its potential as a diagnostic marker. They also found that reactivating BASP1 may suppress B-ALL cell proliferation by inducing DNA damage. Overall, this research provides novel insights and potential therapeutic targets for the diagnosis and treatment of B-ALL.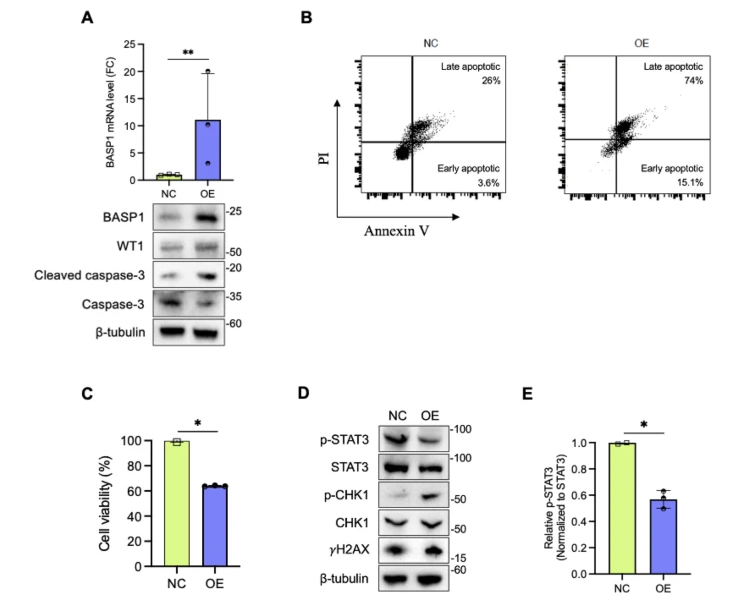
Inhibition of B-ALL cell progression by BASP1 overexpression.
成人B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病(B-ALL)是一种侵袭性恶性肿瘤,临床上完全缓解率有所提高但复发仍是重大挑战。草莓视频 总医院的于力教授团队通过分析患者的表观遗传和转录组数据,发现BASP1启动子区域的高甲基化与成人B-ALL患者的复发密切相关,并可能作为一种诊断标志物。研究还表明,BASP1的重新激活可以通过诱导DNA损伤来抑制B-ALL细胞的增殖。这项研究为B-ALL的诊断和治疗提供了新的视角和潜在的靶点。

Pro. Li Yu
全文链接://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00151-1
4. Efficient analysis of the toxicity and mechanisms of Hexaconazole and two other triazole fungicides: insights from integrated network toxicology, molecular docking and bioinformatics data | Xingke Zhu & Qing Lv
Triazole fungicides, widely used in agriculture, may pose long-term health risks by disrupting the nervous system and liver metabolic pathways. Now, Dr. Xingke Zhu and his team at Hubei University of Chinese Medicine have used a combination of network toxicology, molecular docking, and bioinformatics to investigate the potential toxicity and underlying mechanisms of three triazole fungicides—hexaconazole, propiconazole, and prothioconazole—on the brain and liver. Their findings indicate that the toxicity of these compounds is primarily associated with neurotoxicity and liver damage, with several biological targets identified through database analysis. Molecular docking simulations revealed strong binding between the fungicides and core targets, suggesting these interactions may contribute to brain and liver injury. This study provides a theoretical foundation for understanding triazole fungicide toxicity and highlights the need for further research into their effects on human health.
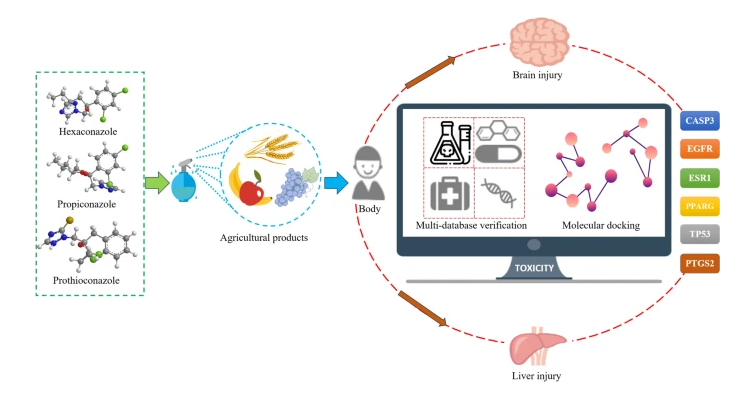
Efficient analysis of the toxicity and mechanisms of Hexaconazole and two other triazole fungicides: insights from integrated network toxicology, molecular docking and bioinformatics data
三唑类杀菌剂是一类广泛用于农业的化学物质,对神经系统和肝脏代谢途径的干扰可能对其长期健康产生不良影响。湖北中医药大学的Xingke Zhu博士团队通过结合网络毒理学、分子对接和生物信息学分析,研究了三种三唑类杀菌剂己唑醇、丙硫菌唑和噻呋菌唑对大脑和肝脏的潜在毒性及其分子机制。 研究发现这些杀菌剂的毒性主要与神经毒性和肝损伤相关,并通过数据库和分析工具识别出多个潜在的生物靶点。分子对接模拟显示杀菌剂与核心靶点具有高亲和力结合,表明它们可能通过与特定蛋白质相互作用诱导脑和肝损伤。该研究为理解三唑类杀菌剂的毒性机制提供了理论基础,并强调了进一步研究其对人类健康影响的必要性。
全文链接: //link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00155-x
5. HDAC6 as a therapeutic target for HPV E7-driven cervical cancer| Wanqing Jiang, Shanshan Liu, Li Fu
Cervical cancer, the fourth most common cancer among women worldwide, is closely associated with persistent infection by high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV). Here, Prof. Li Fu and her team at the Second Hospital of Jilin University have reviewed the role of HDAC6 in cervical cancer. They explain how HDAC6 promotes tumor progression by regulating key cellular processes such as cytoskeletal dynamics, autophagy, the cell cycle, and apoptosis. It also enhances cell motility and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) through the deacetylation of α-tubulin, thereby contributing to tumor invasion and metastasis. These findings underscore the broad therapeutic potential of HDAC6 inhibitors in cervical cancer treatment.
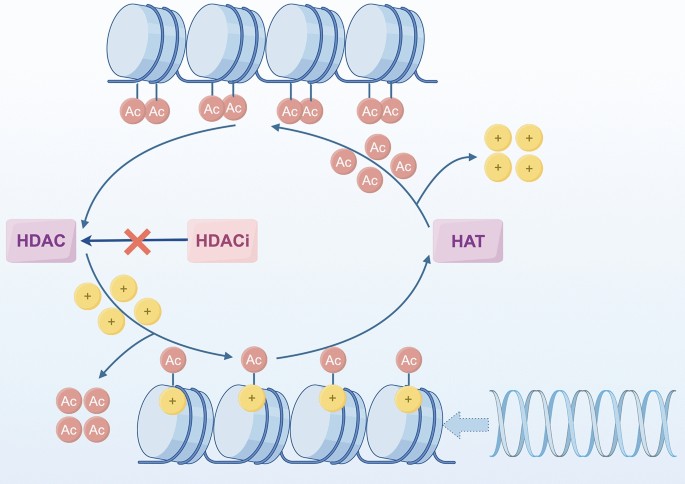
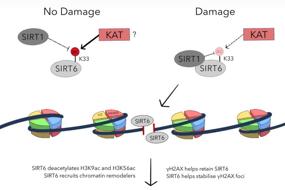
Mechanism involving HDAC and HAT in DNA regulation. HDACs remove acetyl groups (Ac) from histones, leading to a more compact chromatin structure.
宫颈癌是全球女性第四大常见癌症,与高危型人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)持续感染密切相关。来自吉林大学第二附属医院的付莉教授和同事向我们总结了HDAC6 在宫颈癌中的作用,提出HDAC6 可调节细胞骨架动态、自噬、细胞周期和凋亡等过程,促进肿瘤进展。通过去乙酰化 α- 微管蛋白等影响细胞运动性和 EMT,加剧肿瘤侵袭和转移,提示HDAC6 抑制剂在宫颈癌治疗中的广泛前景
Prof. Li Fu
全文链接: //link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00154-y
6. Fetuin-A: A novel protector of hematopoietic stem cell genomic stability | Longjiang Di & Wei-Guo Zhu
In the early stages of liver development, hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) are exposed to a highly genotoxic environment and are particularly vulnerable to genomic instability. Here, Longjiang Di and Professor Wei-Guo Zhu from the Shenzhen University School of Medicine discuss the latest findings by Dengli Hong et al. published in Nature, that offer a new perspective for understanding the mechanisms of genomic protection in embryonic liver development. They focus on the discovery that fetal hepatocytes secrete the protein Fetuin-A, which helps protect the genomic stability of HSPCs and support the proper maturation and development of the fetal liver. Moreover, they highlight that Fetuin-A levels in the bone marrow and serum of infants with leukemia are significantly lower, suggesting a potential link between Fetuin-A deficiency and the development of childhood leukemia.
在肝脏发育的早期阶段,造血干细胞和祖细胞(HSPCs)暴露于高度遗传毒性的环境中,特别容易受到基因组不稳定的影响。在这里,来自草莓视频 的邸龙江博士和朱卫国教授讨论了洪登礼等人发表在《自然》杂志上的最新发现,这些发现为理解胚胎肝脏发育中的基因组保护机制提供了新的视角。他们专注于发现胎儿肝细胞分泌Fetuin-A蛋白,这有助于保护HSPCs的基因组稳定性,并支持胎儿肝脏的适当成熟和发育。此外,他们强调,患有白血病的婴儿骨髓和血清中的胎蛋白-A水平显著降低,这表明胎蛋白-A缺乏与儿童白血病的发展之间存在潜在联系。

Prof. Wei-Guo Zhu
全文链接: //link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00153-z

用户登录
还没有账号?
立即注册